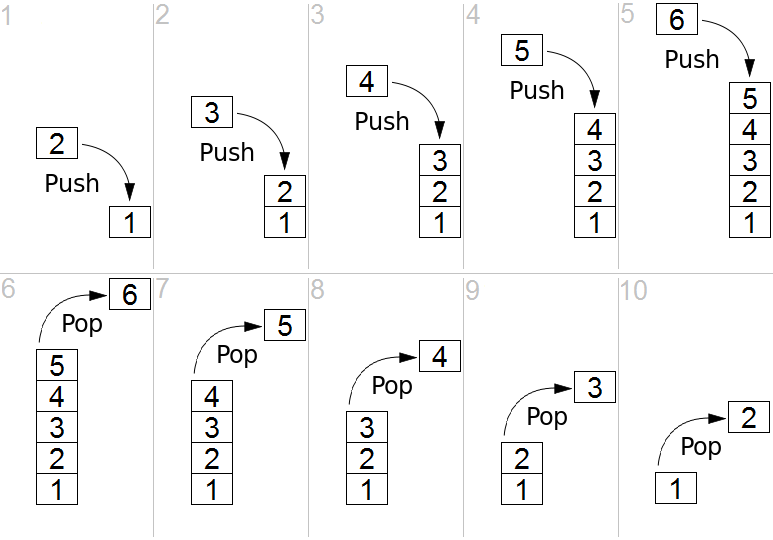
Stack
A stack is a data structure that consists of Nodes. Each Node references the next Node in the stack, but does not reference its previous.
Common terminology for a stack is
- Push - Nodes or items that are put into the stack are pushed
- Pop - Nodes or items that are removed from the stack are popped. When you attempt to pop an empty stack an exception will be raised.
- Top - This is the top of the stack.
- Peek - When you peek you will view the value of the top Node in the stack. When you attempt to peek an empty stack an exception will be raised.
- IsEmpty - returns true when stack is empty otherwise returns false.
- LIFO - Last In First Out
Stacks follow these concepts:
- FILO (First In Last Out) : The first item added in the stack will be the last item popped out of the stack.
- LIFO (Last In First Out) : The last item added to the stack will be the first item popped out of the stack.
Push O(1)
Pushing a Node onto a stack will always be an O(1) operation. This is because it takes the same amount of time no matter how many Nodes (n) you have in the stack.
When adding a Node, you push it into the stack by assigning it as the new top, with its next property equal to the original top.
Pop O(1)
Popping a Node off a stack is the action of removing a Node from the top. When conducting a pop, the top Node will be re-assigned to the Node that lives below and the top Node is returned to the user.
Typically, you would check isEmpty before conducting a pop. If isEmpty returns true, an exception is raised because you are attempting to pop an empty stack.
Peek O(1)
When conducting a peek, you will only be inspecting the top Node of the stack.
Typically, you would check isEmpty before conducting a peek. If isEmpty returns true, an exception is raised because you are attempting to peek an empty stack.
IsEmpty O(1)
Here is the pseudocode for isEmpty
ALGORITHM isEmpty()
// INPUT <-- none
// OUTPUT <-- boolean
return top = NULL
Stack Implementation
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.top = null;
}
push(value) {
const node = new Node(value);
node.next = this.top;
this.top = node;
}
pop() {
if (!this.top) {
throw new Error('Stack is empty');
}
const temp = this.top;
this.top = this.top.next;
temp.next = null;
return temp.value;
}
peek() {
if (!this.top) {
throw new Error('Stack is empty');
}
return this.top.value;
}
isEmpty() {
return !this.top;
}
}
Queue
A queue is a data structure that consists of Nodes. Each Node references the next Node in the queue, but does not reference its previous.

Common terminology for a queue is
- Enqueue - Nodes or items that are added to the queue.
- Dequeue - Nodes or items that are removed from the queue. If called when the queue is empty an exception will be raised.
- Front - This is the front/first Node of the queue.
- Rear - This is the rear/last Node of the queue.
- Peek - When you peek you will view the value of the front Node in the queue. If called when the queue is empty an exception will be raised.
- IsEmpty - returns true when queue is empty otherwise returns false.
- FIFO - First In First Out
Queues follow these concepts:
- FIFO (First In First Out) : The first item added in the queue will be the first item popped out of the queue.
- LILO (Last In Last Out) : The last item added to the queue will be the last item popped out of the queue.
Enqueue O(1)
When you add an item to a queue, you use the enqueue action. This is done by assigning the rear to the new Node and referencing the previous rear to the new rear.
Dequeue O(1)
When you remove an item from a queue, you use the dequeue action. This is done by re-assigning the front to the next Node in the queue.
Typically, you would check isEmpty before conducting a dequeue. If isEmpty returns true, an exception is raised because you are attempting to dequeue an empty queue.
Peek O(1)
When conducting a peek, you will only be inspecting the front Node of the queue.
Typically, you would check isEmpty before conducting a peek. If isEmpty returns true, an exception is raised because you are attempting to peek an empty queue.
IsEmpty O(1)
Here is the pseudocode for isEmpty
ALGORITHM isEmpty()
// INPUT <-- none
// OUTPUT <-- boolean
return front = NULL
Queue Implementation
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.front = null;
this.rear = null;
}
enqueue(value) {
const node = new Node(value);
if (!this.front) {
this.front = node;
this.rear = node;
return;
}
this.rear.next = node;
this.rear = node;
}
dequeue() {
if (!this.front) {
throw new Error('Queue is empty');
}
const temp = this.front;
this.front = this.front.next;
temp.next = null;
return temp.value;
}
peek() {
if (!this.front) {
throw new Error('Queue is empty');
}
return this.front.value;
}
isEmpty() {
return !this.front;
}
}
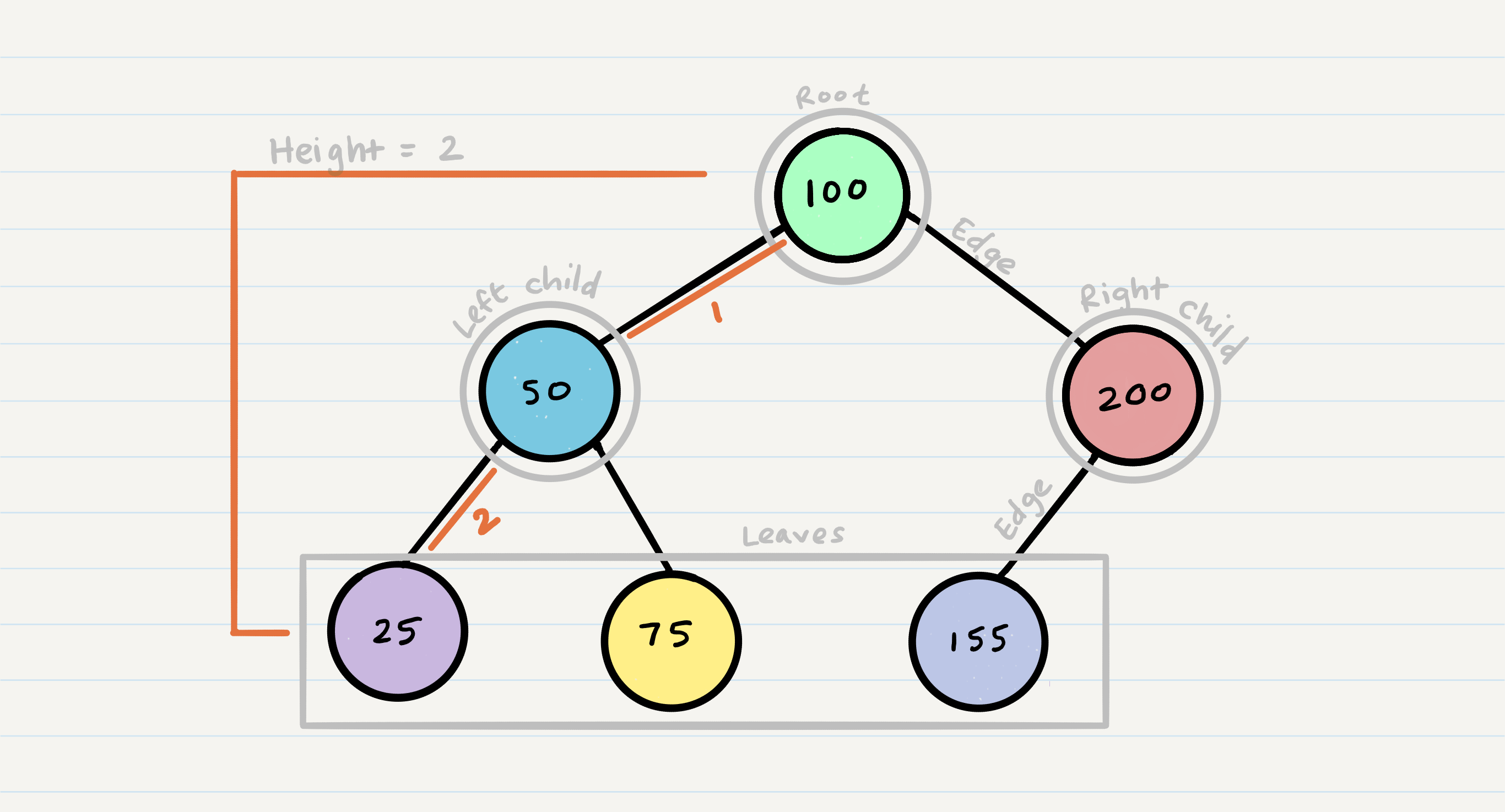
Trees
A tree is a data structure that consists of nodes in a parent/child relationship.
Common Terminology
- Node - A Tree node is a component which may contain it’s own values, and references to other nodes
- Root - The root is the node at the beginning of the tree
- K - A number that specifies the maximum number of children any node may have in a k-ary tree. In a binary tree, k = 2.
- Left - A reference to one child node, in a binary tree
- Right - A reference to the other child node, in a binary tree
- Edge - The edge in a tree is the link between a parent and child node
- Leaf - A leaf is a node that does not have any children
- Height - The height of a tree is the number of edges from the root to the furthest leaf
- K-ary Trees - A k-ary tree is a tree in which each node has up to k children
Traversals
-
Depth First - prioritizes going through the depth (height) of the tree first. There are multiple ways to carry out depth first traversal, and each method changes the order in which we search/print the root.
- Pre-order - root » left » right
- In-order - left » root » right
- Post-order - left » right » root
-
Breadth First - iterates through the tree by going through each level of the tree node-by-node.