Linked-list
The principal benefit of a linked list over a conventional array is that the list elements can easily be inserted or removed without reallocation of any other elements.
In some programming languages, the size of an array is a concern and one of the ways to overcome that problem and allow dynamically allocated data is using linked lists. Luckily in Javascript, arrays aren’t limited to a certain size, so you don’t have to think about overcoming that limitation.
Structure of a Linked List
A linked list is a linear collection of data elements called nodes that “point” to the next node by means of a pointer.
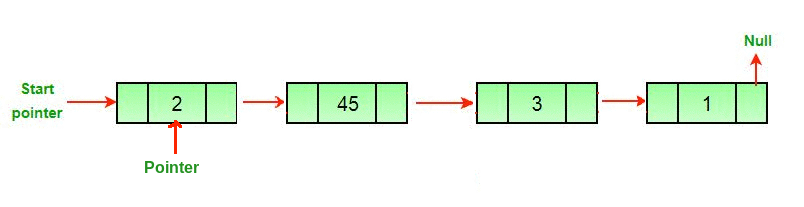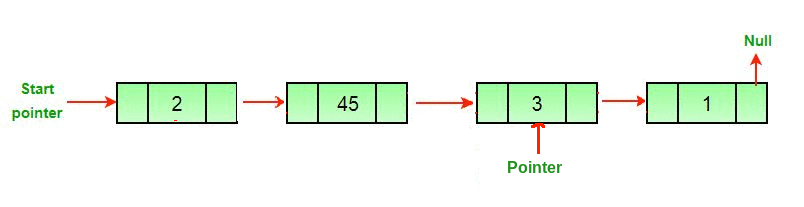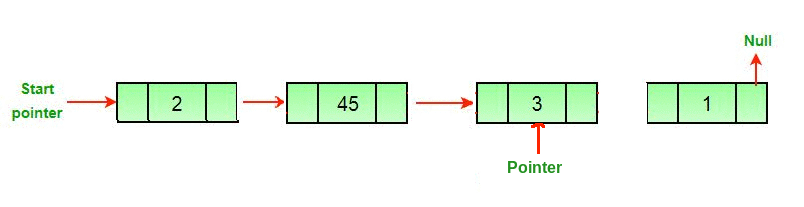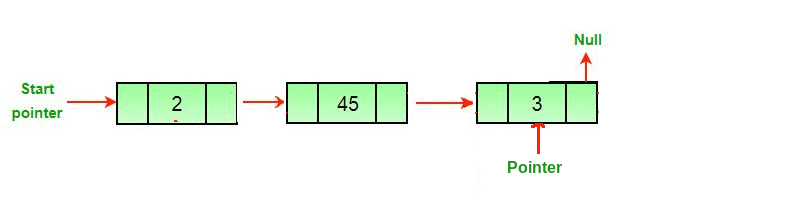
Each node holds a single element of data and a link or pointer to the next node in the list.
A head node is the first node in the list, a tail node is the last node in the list. Below is a basic representation of a linked list:
[ NODE(head) ] -> [ NODE ] -> [ NODE(tail) ] -> null
They are linear data structures, which means that there is a sequence and an order to how they are constructed and traversed.