Binary search
Binary search works on sorted arrays. Binary search begins by comparing an element in the middle of the array with the target value. If the target value matches the element, its position in the array is returned. If the target value is less than the element, the search continues in the lower half of the array. If the target value is greater than the element, the search continues in the upper half of the array. By doing this, the algorithm eliminates the half in which the target value cannot lie in each iteration.

- Its a divide and conquer algorithm
- It only works on sorted arrays
Procedure
Lets say we have an array of numbers [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] and we want to find the index of the number 8
- start point: index = [0]
- end point: index = [9]
- Calculate the middle of the array by adding the start and end point and dividing by 2
middle = (0 + 9) / 2 = 4.5middle = [4](round down)
- Check if the middle is the number we are looking for, if target is met stop.
- Otherwise, if the target is less than the middle, change the end point to be just to the left of the middle(eliminate the right half of the array)
- Otherwise, if the target is greater than the middle, change the start point to be just to the right of the middle(eliminate the left half of the array)
- the element at index [4] is 5, 8 is greater than 5 so we eliminate the left half of the array
- start point:
index = [5]
- Repeat steps 1 - 4 until the target is found or (sub)array is empty
Binary search tree
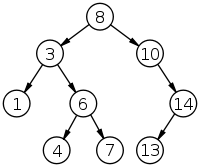
Also called an ordered or sorted binary tree, is a rooted binary tree data structure with the key of each internal node being greater than all the keys in the respective node’s left subtree and less than the ones in its right subtree.
Binary tree traversal
The process of visiting each node in the tree exactly once in some order. Based on the order in which the nodes are visited, there are two types of tree traversal:
- Breadth-first traversal
- Depth-first traversal
- Breadth-first traversal(level order traversal)
- Visit all the nodes at the same level(left to right) before going to the next level
- Code implementaion uses queue
- Breadth-first traversal

- Depth-first traversal
- If we visit a child we must visit all of its descendants before going to the next sibling
- Code implementation uses stack(context stack)
- There are three types of depth-first traversal:
- Pre-order traversal:
root -> left -> right - In-order traversal:
left -> root -> right(inorder traversal of a binary search tree will always give you a sorted list) - Post-order traversal:
left -> right -> root
- Pre-order traversal:
- Depth-first traversal
