Classes and Objects
- Object-oriented programs use objects.
- An object is a thing, both tangible and intangible (e.g., Account, Vehicle, Employee).
- To create an object inside the computer program, we must provide a definition for objects — how they behave and what kinds of information they maintain — called a class.
- An object is called an instance of a class.
Example
// Example of a class definition in Java
public class MyClass {
private int myData; // Private field
public int getMyData() { // Public method to access the private field
return myData;
}
public void setMyData(int value) { // Public method to modify the private field
myData = value;
}
}
In the example, MyClass is a class that defines an object with a private field myData and public methods to access and modify that field.
Main Concepts of OOP
There are 4 main concepts of object-oriented programming:
- Inheritance
- Encapsulation
- Polymorphism
- Abstraction
Inheritance
- Inheritance is a mechanism where you can derive a class from another class to create a hierarchy of classes that share a set of attributes and methods.
- It provides code reusability.
Inheritance Class Diagram
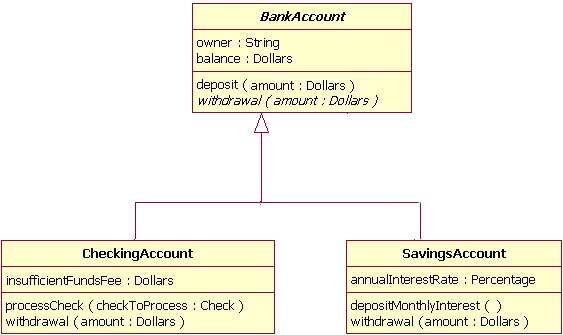
Encapsulation
- Encapsulation describes the idea of bundling data and methods that work on that data within one unit, e.g., a class in Java, a module in Python, or a procedure in C.
- This concept is also often used to hide the internal representation or state of an object from the outside. This is called information hiding.
Example
public class Car {
private String name;
private double topSpeed;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getTopSpeed() {
return topSpeed;
}
public void setTopSpeed(double topSpeed) {
this.topSpeed = topSpeed;
}
public double getTopSpeedMPH() {
return topSpeed * 0.6214;
}
public void setTopSpeedMPH(double topSpeed) {
this.topSpeed = topSpeed / 0.6214;
}
}
The Car class has two fields – name and topSpeed. Both are declared as private, meaning they can not be accessed directly outside the class. The getter and setter methods (getName, setName, setTopSpeed, etc.) are declared public. Those methods are exposed to “outsiders” and can be used to change and retrieve data from the Car object.
Polymorphism
- Polymorphism occurs when a task can be performed in different ways.
- In Java, we use method overloading and method overriding to achieve polymorphism.
Example
class Bank {
float getRateOfInterest() {
return 0;
}
}
class SBI extends Bank {
float getRateOfInterest() {
return 8.4f;
}
}
class ICICI extends Bank {
float getRateOfInterest() {
return 7.3f;
}
}
class AXIS extends Bank {
float getRateOfInterest() {
return 9.7f;
}
}
class TestPolymorphism {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Bank b;
b = new SBI();
System.out.println("SBI Rate of Interest: " + b.getRateOfInterest());
b = new ICICI();
System.out.println("ICICI Rate of Interest: " + b.getRateOfInterest());
b = new AXIS();
System.out.println("AXIS Rate of Interest: " + b.getRateOfInterest());
}
}
Abstraction
- Abstraction involves hiding internal details and showing functionality.
- In Java, we use abstract classes and interfaces to achieve abstraction.
Software Engineering
- Much like building a skyscraper, we need a disciplined approach in developing complex software applications.
- Software engineering is the application of a systematic and disciplined approach to the development, testing, and maintenance of a program.
Software Life Cycle
- The sequence of stages from conception to operation of a program is called the software life cycle.
- Five stages are:
- Analysis
- Design
- Coding
- Testing
- Operation and Maintenance
OOP vs. Procedural Programming
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm that uses objects and classes for organizing code, while Procedural Programming relies on procedures and functions. Two examples of popular object-oriented programming languages are Java and C++. Some other well-known object-oriented programming languages include Objective C, Perl, Python, Javascript, Simula, and Modula.
Procedural programming languages include C, FORTRAN, Pascal, and BASIC.
Advantages and Disadvantages of OOP
Advantages
- Improved software-development productivity: Object-oriented programming is modular, as it provides separation of duties in object-based program development. It is also extensible, as objects can be extended to include new attributes and behaviors. Objects can also be reused within and across applications.
- Improved software maintainability: For the reasons mentioned above, object-oriented software is also easier to maintain. Since the design is modular, part of the system can be updated in case of issues without a need to make large-scale changes.
- Faster development: Reuse enables faster development. Object-oriented programming languages come with rich libraries of objects, and code developed during projects is also reusable in future projects.
- Lower cost of development: The reuse of software also lowers the cost of development. Typically, more effort is put into the object-oriented analysis and design, which lowers the overall cost of development.
- Higher-quality software: Faster development of software and lower cost of development allow more time and resources to be used in the verification of the software. Although quality is dependent upon the experience of the teams, object-oriented programming tends to result in higher-quality software.
Disadvantages
- Steep learning curve: The thought process involved in object-oriented programming may not be natural for some people, and it can take time to get used to it. It is complex to create programs based on the interaction of objects. Some key programming techniques, such as inheritance and polymorphism, can be challenging to comprehend initially.
- Larger program size: Object-oriented programs typically involve more lines of code than procedural programs.
Please insert any images separately with the respective image URLs.